VS Parthasarathy, group chief financial officer of auto and farm equipment maker Mahindra & Mahindra (M&M), recalls a conversation with a supplier a few years back that was one of the inspirations behind MSquare Alliance, an online portal to help small and medium enterprises make acquisitions. It was just after M&M had pulled off an overseas buyout and the supplier let on that he too was pursuing an inorganic strategy for growth.
MSquare Alliance is a forum for the Mahindra ecosystem that helps smaller companies conclude deals by providing them with support services. M&M has a three-member team managing the service, which is free for Mahindra’s dealers and suppliers and is available for a fee for any other company. Operational since 2013, the service, says Parthasarathy, has picked up the pace in the last year. “There is a tsunami of M&A happening below the radar,” Parthasarathy told ET Magazine. “There are people who you and I do not get to meet, who are striking deals for growth.”
Two big deals in the past eight-nine months didn’t, however, escape the radar — both from the Aditya Birla Group. In August 2016, the conglomerate announced the merger of Grasim and Aditya Birla NuvoBSE 2.18 %, creating a Rs 60,000 crore behemoth. The deal got shareholder approval in April 2017. In between, in March, a $27 billion merger of Idea Cellular and Vodafone India was announced, which will create the largest Indian telecom company. Neither was technically a takeover or a buyout, but Sushil Agarwal, Aditya Birla Group CFO, insists that both transactions were done with an eye on growth. The Grasim-Nuvo merger was designed to provide Nuvo’s growth business, the financial services subsidiary, “a stronger parentage” of Grasim’s balance sheet. The Idea-Vodafone deal, too, sacrificed control — Vodafone will hold 45.1% of the merged entity and the Aditya Birla group 26% — and prepped it up for growth and competition, namely Reliance Jio.
Are Indian companies ready to grow through the inorganic route again? Will we see a few daring deals once again?
Veteran industrialist Adi Godrej feels India Inc is brimming with confidence. “In good times people tend to look towards inorganic growth. Generally, the economy is improving, GST will add to growth and banks are also flush with funds. Indian companies will be more open to acquisitions,” says Godrej, chairman of the Godrej Group and a former head of industry body Confederation of Indian Industry.

The Grasim-Nuvo merger that seeks to bring the two Aditya Birla Group giants together has been a deal-in-waiting for a while. Raj Balakrishnan, head of investment banking at DSP Merrill Lynch, who advised Grasim, says: “It is an idea that we were discussing with the Aditya Birla Group for some time.” Investment banking sources reveal that not just Merrill Lynch but many other bankers had been pitching the idea to the head honchos of the group for a few years. It was a natural step to consolidation but, apparently, it had to wait for the right time. Group CFO Agarwal says: “It is always a question of how you feel. Even if you are buying a shirt, you might postpone the transaction if you are not feeling right.”
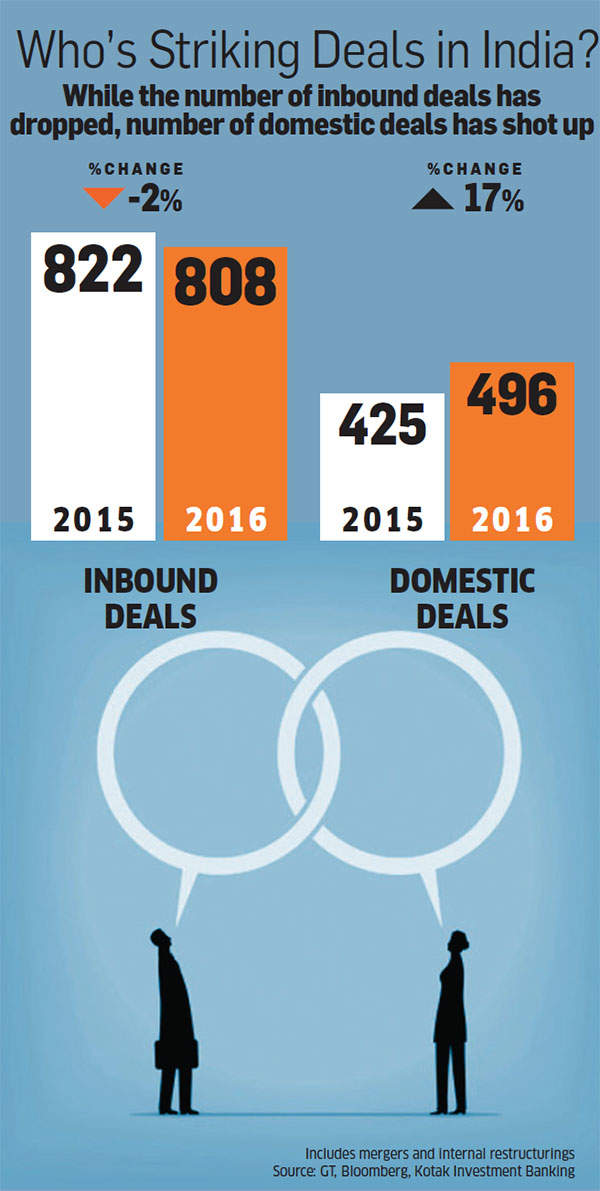
The feel-good factor is definitely a plus right now. Sourav Mallik, joint managing director of Kotak Investment Banking, says he has seen a steady growth in confidence among Indian promoters in the last 12-24 months and it reflects in the growth in domestic deals. “Growth in domestic deals has been much higher compared with inbound deals for buying Indian assets,” says Mallik. The Kotak Group itself pulled a surprise in late April when it bought out the 26% stake of Old Mutual in its joint venture life insurance company for Rs 1,292 crore. An investment banker in the know told ET Magazine that in fact, British insurer Old Mutual had been in the game for a while, trying to buy a larger stake for itself in the company — possibly taking it up to 49%. The reverse deal — where Kotak bought Old Mutual out of the JV — came as a surprise.
Also, there was one announcement from London in March 2017 that boosted sentiments in India. Anil Agarwal, founder of Vedanta Resources, announced that he would pick up a 13% stake in South African miner Anglo American for $2.4 billion. Though not strictly an Indian company, as Vedanta Resources is based and listed in London, the rub-off on India Inc is undeniable as the company has strong roots back home.

The M&A surge is coming at a time when corporations — many of them weighed down by stressed assets — are in no mood to invest. With demand still to pick up in key capital-intensive industrial sectors like steel and cement, capacities created are not being used up — the cement sector, for instance, is working at a utilisation level of 70%. It’s in such times of muted capital expenditure that acquisitions make even more sense. For one, assets — from power, steel and cement factories to airports, roads, and ports — are on offer at fire-sale levels. “Debt-laden companies will have to sell to get out of the mess — and then someone will have to buy,” points out Godrej.
For another, with excess capacity in the system, consolidation is an infinitely more attractive alternative to building new factories. “Inorganic growth makes good sense over organic growth when there is overcapacity in the sector,” says Sushil Agarwal. The Aditya Birla Group acquired Jaypee Group’s cement assets in 2016.
The difference today from the buyout binges a decade ago is that the sky is not the limit — today, for acquisitions from India, the limit is set much lower. A repeat of the days of buying larger global players like Hindalco’s purchase of Novelis for $6 billion or Tata Steel’s $11.3 billion acquisition of Corus is unlikely. Amitabh Malhotra, managing director of Rothschild India, says: “We will never go back to the era of 2006-07 when Indian companies bought our larger global companies. Today the bite size is much smaller.” Average outbound deal size in 2016 was $ 63 million.
Picking Up Themes
However, that does not mean there is respite for Malhotra. Interest from global private equity (PE) players in Indian assets is at a peak although deal numbers are low right now (PE is one of Malhotra’s areas of expertise). One person who agrees with Malhotra is Prashant Mehra, partner of Grant Thornton India who also works on the firm’s quarterly deal tracker. Mehra feels that a new PE wave is in the offing where it will be looked at as an alternative means of funding domestic consolidation. He points out that among the many things going for India is a strong domestic economy —ADB estimates India to grow at 7.2% in 2017-18 and 7.7% in 2018-19 — and that sets it apart from other markets in the region. “The strong domestic Indian economy today is a very different story than China’s,” says Mehra.
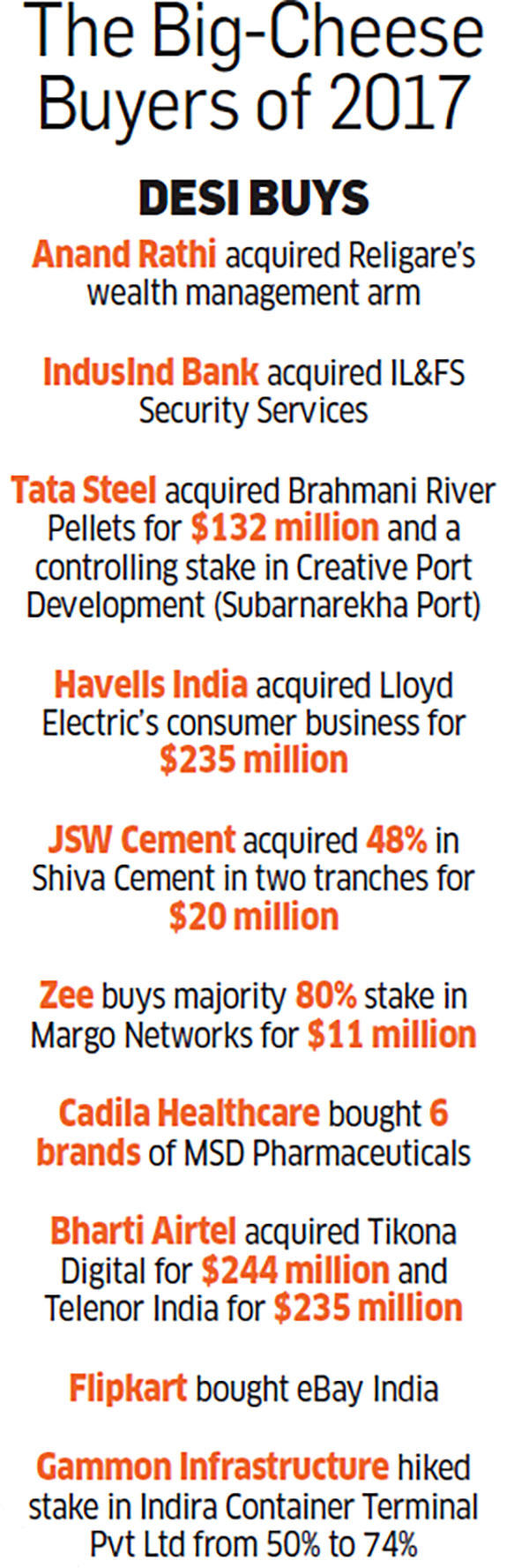
The attractions of the Indian economy are just one of the themes in the works right now. There are other themes like acquisition of a new product as done by the Indian pharma giants or acquiring market share as demonstrated by the Flipkart-eBay India deal. Then there are technology and people plays, especially when companies are buying abroad.
Other triggers include a global major’s exit due to problems in their domestic market — for instance, Lafarge India, which was grappling with debt and lower global demand after the merger with Holcim, chose to sell its Indian cement assets to Nirma last July for $1.4 billion. And as the Vodafone India-Idea merger shows, if growth and taking on competition are priorities, who’s in the driving seat is less important. Ausang Shukla, managing director, corporate finance, at Ambit Capital, agrees that stress-related M&A is a clear theme. “Indian promoters are not hung up on control anymore. They are more amenable to being smaller shareholders of a larger business,” says Shukla.
This is Shukla’s second stint at Ambit as investment banker, and he says he has made a wise choice, joining an Indian firm focused on the Indian market as that is where the action will be.
While global buys are often for technology — and Mahindra and Wipro have gone in for such buys — another round of investments and acquisitions, for technology and people, is flowing from large Indian conglomerates into Indian startups. Says Parthasarathy of M&M: “Today one cannot ignore the startups and the capabilities that startup teams can bring in.” He says that in order to keep pace with developments, M&M has not just acquired larger or mature businesses but have also acquired startups and at the same time allowed a corporate garage to flourish, backing independent entrepreneurial ideas.
Or, take the example of Sunil Munjal, who has exited Hero MotoCorp and is building his own group of companies under the brand Hero Enterprise. Munjal admits that the group is likely to expand its portfolio of businesses through acquisitions of large businesses but is yet to do so. At the same time, he lets on that he has invested in or acquired more than a dozen startups. When asked about larger buys to grow his businesses, he says, “It’s best to talk about it when one has done it.”
Caution with Optimism
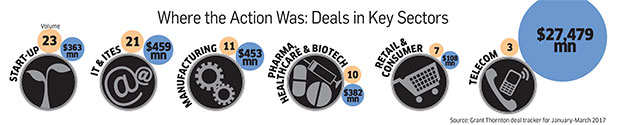
Numbers tell a mixed story. Grant Thornton’s deal tracker shows that domestic takeover deals clocked $13.4 billion in 2016, up from $8.4 billion in 2015, whereas the actual number of domestic takeover deals fell marginally from 321 to 310. Again, if we compare the outbound deals, where Indian companies are buying overseas, the total deal value of 2015 was $6 billion and it went up to $6.3 billion in 2016, but deal numbers came down from 120 in 2015 to 99 in 2016. The first quarter of calendar year 2017, that ended on March 31, also showed similar trends with domestic takeover deal value adding up to $2,558 million ($2,464 million in 2016) and the number of domestic takeover deals recorded in the quarter falling marginally from 66 in 2016 first quarter to 54 in 2017 first quarter. The outbound deal value in the quarter fell drastically to $580 million in 2017 from $2,400 million in 2016 with the number of transactions falling to 22 from 32.
Clearly, the actual deal numbers have not caught up with the enthusiasm all around yet. Not every company is raring to go right now. Parthasarathy of Mahindra says that the group is keeping its “gunpowder dry”, waiting for the right moment for big deals. And Paresh Sukthankar, deputy managing director of HDFC Bank, told ET Magazine in an interview early April that the bank does not need acquisitions to deliver growth. “With our size, acquisition opportunities that can move the needle for us tend to be very few,” he said.
Agarwal of the Aditya Birla Group said that a company going for acquisition has to first ask why it is doing it and whether the business rationale fits, and then it must ask if the balance sheet has enough strength to take it on. It is a pointer to another problem — of funding. Indian banks face restrictions in acquisition financing: for instance, a bank cannot fund a promoter’s contribution towards equity, and it is only in the rarest of cases that banks can finance acquisition of equity shares.
Godrej feels this is wrong. “We have to change such rules. Nowhere in the world are banks told you cannot fund acquisitions. There should be less regulation. Too much regulation creates problems in the way of growth and the economy prospering.”
There is something about India that has everyone excited right now. Probably, there is also an Indian way of doing deals. Rothschild’s India office in Mumbai’s Lower Parel has adopted one of the latest office décor fads in India — an open office — where even the managing director sits in an open area. Apparently, open offices work in India as Indians are more “touchy-feely” in their work habits than, say, people in Southeast Asian countries.
